Mothers are more likely to be at risk of poverty in old age
04.04.21
UN Geneva - In its response to the Human Rights of Older Women consultation, MMM identifies the inequitable distribution of unpaid family caregiving duties between men and women as a root cause of the gender pension gaps.
Make Mothers Matter’s response to the call for contributions on “The Human Rights of older women” issued by the the Independent Expert on the enjoyment of all human rights by older persons Make Mothers Matter responded to the questionnaire on the economic, social and cultural realities faced by older women.
When it comes to receiving an adequate retirement pension, there are significant gaps between men and women around the world. These gaps are of 2 types:
- eligibility to receive a pension
- the level of pensions
Globally, only about half of all people over the legal retirement age receive an old-age pension, and in most countries men are the main beneficiaries. The gap is widest in developing countries. In Egypt and Jordan, for example, men are 7 to 8 times more likely to receive a pension than women.
 Even when women are entitled to a pension, the level of their benefits is lower than that of men – although this gap varies considerably from country to country. For example, in the EU, women’s pensions are on average 29% lower than men’s, but this gap varies from 2% in Estonia to 44% in Luxembourg.
Even when women are entitled to a pension, the level of their benefits is lower than that of men – although this gap varies considerably from country to country. For example, in the EU, women’s pensions are on average 29% lower than men’s, but this gap varies from 2% in Estonia to 44% in Luxembourg.
These pension gaps lead to a higher risk of income insecurity and poverty in old age for women. In addition, they threaten many of their economic and social rights, including the right to health and an adequate standard of living. In the EU, for example, 17% of retired women are considered to be at risk of poverty, compared to 13% of men.
This means that many women lack economic independence in old age, which prevents them from leaving abusive relationships when necessary.
Finally, the increase in women’s life expectancy also increases the likelihood that older women will spend a longer part of their lives alone and poor.
The reasons for these gender gaps in eligibility and benefits are multiple. They include lower labour market participation of women, lower average earnings, and a higher incidence of informal employment.
They are mainly the result of the different working patterns of men and women over the life course. The reality for a majority of families is that it is women/mothers rather than men/fathers who take on care responsibilities. In the majority of cases, mothers prioritise their families to the detriment of their own careers and future pensions, either by taking long career breaks to raise children or by being more likely to work part-time.
These different patterns of work are also linked to an accumulation of discriminations that women face in the economic sphere during their lifetime. These discriminations often join other types of discrimination (such as race and ethnicity, age, migratory status, urban/rural, maternity, etc.) :
- Access to the formal labour market (which forces women to work in the informal sector)
- Access to social protection, often linked to formal employment (starting with maternity protection, but also access to health care, social security…)
- Access to economic resources (land, financial services, technology…)
- Discrimination in the workplace (gender pay gap, access to decision-making positions, low quality part-time jobs)
- Occupational segregation: women are over-represented in low-paid occupations (domestic work, health care, education…)
The inequitable division of unpaid family care work between men and women is at the root of many, if not all, of the inequalities and discrimination that women face throughout their lives. According to the former Special Rapporteur on extreme poverty and human rights, Magdalena Sepulveda, “the gendered division of unpaid care work is one of the main reasons why older women are more likely to live in poverty than their male counterparts.”
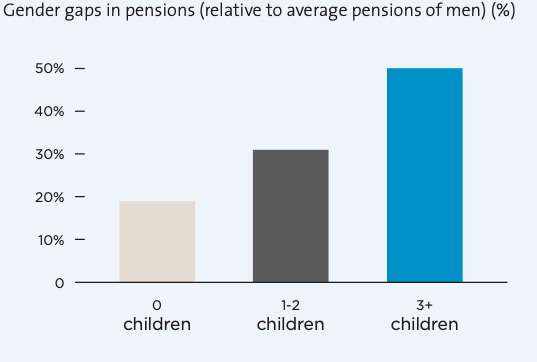
In France, the gender gap in pension benefits is larger for mothers – Source: UN Women
And mothers are particularly penalised: not only because they interrupt their careers to bring up their children, but also because the M-F wage gap is greater for mothers than for women without children. As a result, pension gaps are higher for mothers than for women who have not had children. In France, for example, the M-F pension gap reaches 48% for mothers with 3 or more children, compared to 18% for women without children.
Time use surveys show that when paid and unpaid work is combined, women work more than men. Addressing the issue of unpaid care work, including the recognition of the essential value of this work to our economy and society, is therefore essential to empower women and to address the income insecurity and vulnerability to poverty of older women.
One way to achieve this is to implement ‘care credits’ in pension systems, which are detailed in our response to the consultation.
MMM’s Response to the consultation

Mothers, unpaid care work and global crises – connecting the dots
02.07.24
UN New York / HLPF - Register now to join us online at this year’s High Level Political Forum side-event.
Time Poverty and the Motherhood Penalty
Unveiling Economic and Social Injustices
09.07.24
Mothers play an essential role in families by ensuring their loved ones are nourished, educated, and healthy, but their unpaid care work often leads to economic and social injustices, known
Envisioning care as a common thread to global crises
29.07.24
UN New York - Our virtual HLPF side-event brought together experts to shed light on how the various global crises we face (in particular climate change and other environmental crises,