Discriminations in the economic sphere: the “motherhood penalty”
All over the world, women suffer, to varying degrees, from discrimination that hinders their economic empowerment – especially when they are mothers.
Discriminations against women
Legal discriminations
According to the World Bank (report Women, Business and the Law, 2016):
- Only 18 countries have no laws that disadvantage or discriminate women.
- In 35 countries, women who survive their spouses do not have the same inheritance rights as men, so they do not have the same rights to access property.
- In 18 countries, women need permission from their husband to work.
- In 16 countries, taxation directly favours men.
- Only 9 countries have enacted laws requiring that at least one woman sits on the board of directors of publicly traded companies.
- In 167 countries, maternity leave is compulsory, and 86 countries have also introduced paternity leave, but only 51 countries offer parental leave.
Social discrimination
Many forms of discrimination against women are linked to deeply rooted cultural prejudices and stereotypes about their role in society. For example:
- Access to education and training
- Access to the labour market (formal employment) and social protection
- Access to property (including land) and inheritance
- Access to credit and financial services
- The level of remuneration.
Occupational segregation
Women most often have less skilled, less paid and more precarious jobs. They are mainly present in less profitable sectors. like health, education, social work or retail sales. Women are also notoriously underrepresented in more valued sectors like technology or finance.
Overrepresentation in the informal sector

Mother, street vendor in Myanmar – Photo by Laurence vanden Abeele
Women Labour Force Participation Rate remains much lower than that of men: overall, 75.1% of men are employed, a percentage that falls to 49.6% for women.
On the other hand, women are overrepresented in the informal sector, especially in developing countries or when migrating. They are all too often “self-employed” as street vendors, domestic helpers, seasonal workers, or subsistence farmers, etc.
According to UN Women, more than 80% of women in South Asia who do not work in the agricultural sector are in informal jobs; in sub-Saharan Africa, they are 74%; in Latin America and the Caribbean, 54%.
Not only these women in the informal sector work for incomes that are systematically lower and under precarious conditions, but they are also deprived of the social protection linked to paid employment – including health insurance, maternity protection and other paid leave, as well a retirement pension.
The “motherhood penalty”
In addition to the barriers they face as women, mothers are also discriminated against in the world of work because of their status as mothers.

Source: UN Women 2016
Such specific discriminations against mothers, i.e. not only compared to men, but compared to women without children, include barriers at hiring, lower remuneration, and obstacles to carrier advancement and access to decision making positions within the company.
This “Motherhood penalty” is increasingly recognized and documented. In 2016, the International Labour Organisation (ILO) published for the first time a report on the “Motherhood wage pay”. This report clearly shows that wage gaps exist not only between men and women, but also between mothers and women who do not have children.
“Mothers around the world face the same crucial pressure of providing financially for their families’ well-being, while also needing to provide the nurturing and caregiving necessities of their household. It is fair to say that globally, mothers have responded to this pressure by working even harder and for more hours, to the detriment of their own personal time. Yet they are still paid significantly less than their male counterparts or childless female cohorts.
It has been suggested that mothers earn less than childless women because they are less productive. In fact, they are penalized for going on maternity leave, for possibly not putting in as much ‘face time’ at work as their childless peers, for having to turn down jobs that require overtime, and for daring to ask for part-time work. They are simply victims of the perception/stereotype that women with children are not as much ‘into’ their jobs as others because they are distracted by the caring and nurturing requirements of their households.”
Extract from MMM Contribution to the book Family Future,
edited by the UN in 2014 for the 20th anniversary of the 20th anniversary of the international year of the family
The gender pension gap shows the extend of the Motherhood penalty
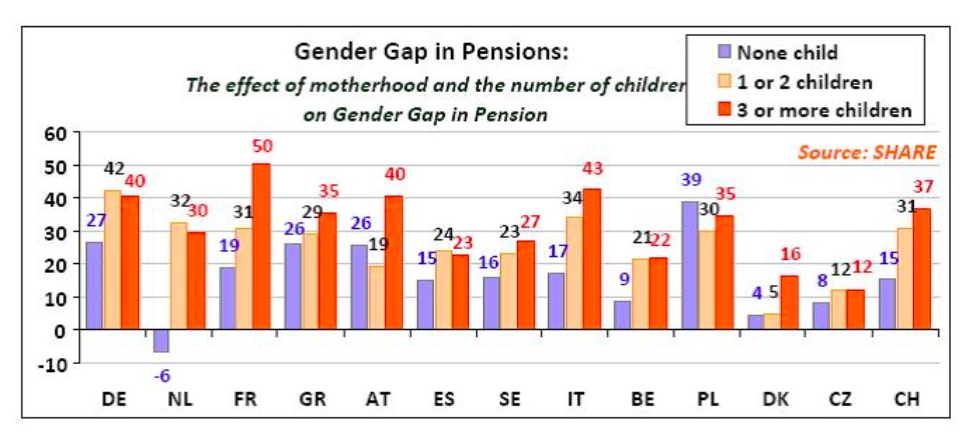
Gender Pension gaps according to the number of children in a selection of EU countries – Source: The Gender Pension Etude de Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Information Technology (FIT) 2013
Differences in retirement pensions between men and women, especially when they are mothers, are the result not only of maternity-related career breaks, but also of the accumulation of all the discriminations they face throughout their working lives.
Can mothers have it all – Family and career?
While men progress most professionally speaking between 30 and 40 years, it is precisely during this age that mothers slow down their career to give priority to their family … And when they come back at 40, it is often too late – Unless they fought tooth and nail to stay in the race!
As the controversy sparked in 2012 by Anne-Marie Slaughter’s article in The Atlantic,, Why women still can’t have it all, has shown, women remain divided on the issue. But basically, a mother should not have to choose. In a context of ageing populations, companies must recognize the potential of mothers, and support their return to the labour market when their children are older.
Businesses, and society as a whole, must accept that women – and men ! – may need, during certain periods of their lives, to slow down or withdraw from their professional life in order to take on family or other responsibilities, and facilitate their return to work after such periods.





